ledger is an R package to import data from plain text accounting software like Ledger, HLedger, and Beancount into an R data frame for convenient analysis, plotting, and export.
Right now it supports reading in the register from ledger, hledger, and beancount files.
To install the last version released to CRAN use the following command in R:
install.packages("ledger")To install the development version of the ledger package (and its R package dependencies) use the install_github function from the remotes package in R:
install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("trevorld/r-ledger")This package also has some system dependencies that need to be installed depending on which plaintext accounting files you wish to read to be able to read in:
ledger
ledger (>= 3.1)
hledger
hledger (>= 1.4)
beancount
beancount (>= 2.0)
To install hledger run the following in your shell:
stack update && stack install --resolver=lts-14.3 hledger-lib-1.15.2 hledger-1.15.2 hledger-web-1.15 hledger-ui-1.15 --verbosity=error To install beancount run the following in your shell:
pip3 install beancountSeveral pre-compiled Ledger binaries are available (often found in several open source repos).
To run the unit tests you’ll also need the suggested R package testthat.
The main function of this package is register which reads in the register of a plaintext accounting file. This package also registers S3 methods so one can use rio::import to read in a register, a net_worth convenience function, and a prune_coa convenience function.
Here are some examples of very basic files stored within the package:
library("ledger")
options(width=180)
ledger_file <- system.file("extdata", "example.ledger", package = "ledger")
register(ledger_file)
## # A tibble: 42 × 8
## date mark payee description account amount commodity comment
## <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
## 1 2015-12-31 * <NA> Opening Balances Assets:JT-Checking 5000 USD <NA>
## 2 2015-12-31 * <NA> Opening Balances Equity:Opening -5000 USD <NA>
## 3 2016-01-01 * Landlord Rent Assets:JT-Checking -1500 USD <NA>
## 4 2016-01-01 * Landlord Rent Expenses:Shelter:Rent 1500 USD <NA>
## 5 2016-01-01 * Brokerage Buy Stock Assets:JT-Checking -1000 USD <NA>
## 6 2016-01-01 * Brokerage Buy Stock Equity:Transfer 1000 USD <NA>
## 7 2016-01-01 * Brokerage Buy Stock Assets:JT-Brokerage 4 SP <NA>
## 8 2016-01-01 * Brokerage Buy Stock Equity:Transfer -1000 USD <NA>
## 9 2016-01-01 * Supermarket Grocery store ;; Link: ^grocery Expenses:Food:Grocery 501. USD <NA>
## 10 2016-01-01 * Supermarket Grocery store ;; Link: ^grocery Liabilities:JT-Credit-Card -501. USD <NA>
## # … with 32 more rows
hledger_file <- system.file("extdata", "example.hledger", package = "ledger")
register(hledger_file)
## # A tibble: 42 × 11
## date mark payee description account amount commodity historical_cost hc_commodity market_value mv_commodity
## <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
## 1 2015-12-31 * <NA> Opening Balances Assets:JT-Checking 5000 USD 5000 USD 5000 USD
## 2 2015-12-31 * <NA> Opening Balances Equity:Opening -5000 USD -5000 USD -5000 USD
## 3 2016-01-01 * Landlord Rent Assets:JT-Checking -1500 USD -1500 USD -1500 USD
## 4 2016-01-01 * Landlord Rent Expenses:Shelter:Rent 1500 USD 1500 USD 1500 USD
## 5 2016-01-01 * Brokerage Buy Stock Assets:JT-Checking -1000 USD -1000 USD -1000 USD
## 6 2016-01-01 * Brokerage Buy Stock Equity:Transfer 1000 USD 1000 USD 1000 USD
## 7 2016-01-01 * Brokerage Buy Stock Assets:JT-Brokerage 4 SP 1000 USD 2000 USD
## 8 2016-01-01 * Brokerage Buy Stock Equity:Transfer -1000 USD -1000 USD -1000 USD
## 9 2016-01-01 * Supermarket Grocery store Expenses:Food:Grocery 501. USD 501. USD 501. USD
## 10 2016-01-01 * Supermarket Grocery store Liabilities:JT-Credit-Card -501. USD -501. USD -501. USD
## # … with 32 more rows
beancount_file <- system.file("extdata", "example.beancount", package = "ledger")
register(beancount_file)
## # A tibble: 42 × 12
## date mark payee description account amount commodity historical_cost hc_commodity market_value mv_commodity tags
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
## 1 2015-12-31 * "" Opening Balances Assets:JT-Checking 5000 USD 5000 USD 5000 USD ""
## 2 2015-12-31 * "" Opening Balances Equity:Opening -5000 USD -5000 USD -5000 USD ""
## 3 2016-01-01 * "Landlord" Rent Assets:JT-Checking -1500 USD -1500 USD -1500 USD ""
## 4 2016-01-01 * "Landlord" Rent Expenses:Shelter:Rent 1500 USD 1500 USD 1500 USD ""
## 5 2016-01-01 * "Brokerage" Buy Stock Assets:JT-Checking -1000 USD -1000 USD -1000 USD ""
## 6 2016-01-01 * "Brokerage" Buy Stock Equity:Transfer 1000 USD 1000 USD 1000 USD ""
## 7 2016-01-01 * "Brokerage" Buy Stock Assets:JT-Brokerage 4 SP 1000 USD 2000 USD ""
## 8 2016-01-01 * "Brokerage" Buy Stock Equity:Transfer -1000 USD -1000 USD -1000 USD ""
## 9 2016-01-01 * "Supermarket" Grocery store Expenses:Food:Grocery 501. USD 501. USD 501. USD ""
## 10 2016-01-01 * "Supermarket" Grocery store Liabilities:JT-Credit-Card -501. USD -501. USD -501. USD ""
## # … with 32 more rowsHere is an example reading in a beancount file generated by bean-example:
bean_example_file <- tempfile(fileext = ".beancount")
system(paste("bean-example -o", bean_example_file), ignore.stderr=TRUE)
df <- register(bean_example_file)
options(width=240)
print(df)
## # A tibble: 3,330 × 12
## date mark payee description account amount commodity historical_cost hc_commodity market_value mv_commodity tags
## <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
## 1 2019-01-01 * "" Opening Balance for checking account Assets:US:BofA:Checking 4119. USD 4119. USD 4119. USD ""
## 2 2019-01-01 * "" Opening Balance for checking account Equity:Opening-Balances -4119. USD -4119. USD -4119. USD ""
## 3 2019-01-01 * "" Allowed contributions for one year Income:US:Federal:PreTax401k -18500 IRAUSD -18500 IRAUSD -18500 IRAUSD ""
## 4 2019-01-01 * "" Allowed contributions for one year Assets:US:Federal:PreTax401k 18500 IRAUSD 18500 IRAUSD 18500 IRAUSD ""
## 5 2019-01-03 * "Hooli" Payroll Assets:US:BofA:Checking 1351. USD 1351. USD 1351. USD ""
## 6 2019-01-03 * "Hooli" Payroll Assets:US:Vanguard:Cash 1200 USD 1200 USD 1200 USD ""
## 7 2019-01-03 * "Hooli" Payroll Income:US:Hooli:Salary -4615. USD -4615. USD -4615. USD ""
## 8 2019-01-03 * "Hooli" Payroll Income:US:Hooli:GroupTermLife -24.3 USD -24.3 USD -24.3 USD ""
## 9 2019-01-03 * "Hooli" Payroll Expenses:Health:Life:GroupTermLife 24.3 USD 24.3 USD 24.3 USD ""
## 10 2019-01-03 * "Hooli" Payroll Expenses:Health:Dental:Insurance 2.9 USD 2.9 USD 2.9 USD ""
## # … with 3,320 more rows
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library("dplyr"))
dplyr::filter(df, grepl("Expenses", account), grepl("trip", tags)) %>%
group_by(trip = tags, account) %>%
summarise(trip_total = sum(amount))
## `summarise()` has grouped output by 'trip'. You can override using the `.groups` argument.
## # A tibble: 7 × 3
## # Groups: trip [3]
## trip account trip_total
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 trip-boston-2020 Expenses:Food:Coffee 6.39
## 2 trip-boston-2020 Expenses:Food:Restaurant 234.
## 3 trip-los-angeles-2021 Expenses:Food:Alcohol 52.6
## 4 trip-los-angeles-2021 Expenses:Food:Coffee 24.3
## 5 trip-los-angeles-2021 Expenses:Food:Restaurant 458.
## 6 trip-san-francisco-2019 Expenses:Food:Coffee 30.0
## 7 trip-san-francisco-2019 Expenses:Food:Restaurant 624.If one has loaded in the ledger package one can also use rio::import to read in the register:
df2 <- rio::import(bean_example_file)
all.equal(df, tibble::as_tibble(df2))
## [1] TRUEThe main advantage of this is that it allows one to use rio::convert to easily convert plaintext accounting files to several other file formats such as a csv file. Here is a shell example:
bean-example -o example.beancount
Rscript --default-packages=ledger,rio -e 'convert("example.beancount", "example.csv")'Some examples of using the net_worth function using the example files from the register examples:
dates <- seq(as.Date("2016-01-01"), as.Date("2018-01-01"), by="years")
net_worth(ledger_file, dates)
## # A tibble: 3 × 6
## date commodity net_worth assets liabilities revalued
## <date> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2016-01-01 USD 5000 5000 0 0
## 2 2017-01-01 USD 4361. 4882 -521. 0
## 3 2018-01-01 USD 6743. 6264 -521. 1000
net_worth(hledger_file, dates)
## # A tibble: 3 × 5
## date commodity net_worth assets liabilities
## <date> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2016-01-01 USD 5000 5000 0
## 2 2017-01-01 USD 4361. 4882 -521.
## 3 2018-01-01 USD 6743. 7264 -521.
net_worth(beancount_file, dates)
## # A tibble: 3 × 5
## date commodity net_worth assets liabilities
## <date> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2016-01-01 USD 5000 5000 0
## 2 2017-01-01 USD 4361. 4882 -521.
## 3 2018-01-01 USD 6743. 7264 -521.
net_worth(bean_example_file, dates)
## # A tibble: 0 × 3
## # … with 3 variables: date <date>, commodity <chr>, net_worth <lgl>Some examples using the prune_coa function to simplify the “Chart of Account” names to a given maximum depth:
suppressPackageStartupMessages(library("dplyr"))
df <- register(bean_example_file) %>% dplyr::filter(!is.na(commodity))
df %>% prune_coa() %>%
group_by(account, mv_commodity) %>%
summarize(market_value = sum(market_value), .groups = "drop")
## # A tibble: 11 × 3
## account mv_commodity market_value
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Assets IRAUSD 0
## 2 Assets USD 119287.
## 3 Assets VACHR 87
## 4 Equity USD -4119.
## 5 Expenses IRAUSD 55500
## 6 Expenses USD 269081.
## 7 Expenses VACHR 288
## 8 Income IRAUSD -55500
## 9 Income USD -377046.
## 10 Income VACHR -375
## 11 Liabilities USD -2248.
df %>% prune_coa(2) %>%
group_by(account, mv_commodity) %>%
summarize(market_value = sum(market_value), .groups = "drop")
## # A tibble: 17 × 3
## account mv_commodity market_value
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Assets:US IRAUSD 0
## 2 Assets:US USD 1.19e+ 5
## 3 Assets:US VACHR 8.7 e+ 1
## 4 Equity:Opening-Balances USD -4.12e+ 3
## 5 Expenses:Financial USD 4.44e+ 2
## 6 Expenses:Food USD 1.87e+ 4
## 7 Expenses:Health USD 7.27e+ 3
## 8 Expenses:Home USD 8.86e+ 4
## 9 Expenses:Taxes IRAUSD 5.55e+ 4
## 10 Expenses:Taxes USD 1.50e+ 5
## 11 Expenses:Transport USD 4.08e+ 3
## 12 Expenses:Vacation VACHR 2.88e+ 2
## 13 Income:US IRAUSD -5.55e+ 4
## 14 Income:US USD -3.77e+ 5
## 15 Income:US VACHR -3.75e+ 2
## 16 Liabilities:AccountsPayable USD 5.68e-14
## 17 Liabilities:US USD -2.25e+ 3Here is some examples using the functions in the package to help generate various personal accounting reports of the beancount example generated by bean-example.
First we load the (mainly tidyverse) libraries we’ll be using and adjusting terminal output:
options(width=240) # tibble output looks better in wide terminal output
library("ledger")
library("dplyr")
filter <- dplyr::filter
library("ggplot2")
library("scales")
library("tidyr")
library("zoo")
filename <- tempfile(fileext = ".beancount")
system(paste("bean-example -o", filename), ignore.stderr=TRUE)
df <- register(filename) %>% mutate(yearmon = zoo::as.yearmon(date)) %>%
filter(commodity=="USD")
nw <- net_worth(filename)Then we’ll write some convenience functions we’ll use over and over again:
print_tibble_rows <- function(df) {
print(df, n=nrow(df))
}
count_beans <- function(df, filter_str = "", ...,
amount = "amount",
commodity="commodity",
cutoff=1e-3) {
commodity <- sym(commodity)
amount_var <- sym(amount)
filter(df, grepl(filter_str, account)) %>%
group_by(account, !!commodity, ...) %>%
summarize(!!amount := sum(!!amount_var), .groups = "drop") %>%
filter(abs(!!amount_var) > cutoff & !is.na(!!amount_var)) %>%
arrange(desc(abs(!!amount_var)))
}Here is some basic balance sheets (using the market value of our assets):
print_balance_sheet <- function(df) {
assets <- count_beans(df, "^Assets",
amount="market_value", commodity="mv_commodity")
print_tibble_rows(assets)
liabilities <- count_beans(df, "^Liabilities",
amount="market_value", commodity="mv_commodity")
print_tibble_rows(liabilities)
}
print(nw)
## # A tibble: 3 × 5
## date commodity net_worth assets liabilities
## <date> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 2021-11-12 IRAUSD 0 0 0
## 2 2021-11-12 USD 123655. 126076. -2421.
## 3 2021-11-12 VACHR 15 15 0
print_balance_sheet(prune_coa(df, 2))
## # A tibble: 1 × 3
## account mv_commodity market_value
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Assets:US USD 6785.
## # A tibble: 1 × 3
## account mv_commodity market_value
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Liabilities:US USD -2421.
print_balance_sheet(df)
## # A tibble: 3 × 3
## account mv_commodity market_value
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Assets:US:ETrade:Cash USD 6297.
## 2 Assets:US:BofA:Checking USD 489.
## 3 Assets:US:Vanguard:Cash USD -0.0200
## # A tibble: 1 × 3
## account mv_commodity market_value
## <chr> <chr> <dbl>
## 1 Liabilities:US:Chase:Slate USD -2421.Here is a basic chart of one’s net worth from the beginning of the plaintext accounting file to today by month:
next_month <- function(date) {
zoo::as.Date(zoo::as.yearmon(date) + 1/12)
}
nw_dates <- seq(next_month(min(df$date)), next_month(Sys.Date()), by="months")
df_nw <- net_worth(filename, nw_dates) %>% filter(commodity=="USD")
ggplot(df_nw, aes(x=date, y=net_worth, colour=commodity, group=commodity)) +
geom_line() + scale_y_continuous(labels=scales::dollar)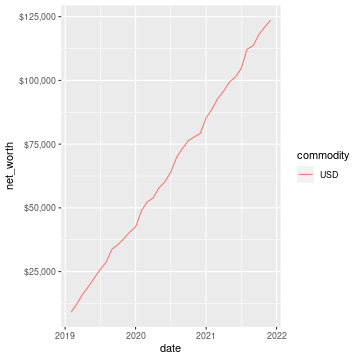
month_cutoff <- zoo::as.yearmon(Sys.Date()) - 2/12
compute_income <- function(df) {
count_beans(df, "^Income", yearmon) %>%
mutate(income = -amount) %>%
select(-amount) %>% ungroup()
}
print_income <- function(df) {
compute_income(df) %>%
filter(yearmon >= month_cutoff) %>%
spread(yearmon, income, fill=0) %>%
print_tibble_rows()
}
compute_expenses <- function(df) {
count_beans(df, "^Expenses", yearmon) %>%
mutate(expenses = amount) %>%
select(-amount) %>% ungroup()
}
print_expenses <- function(df) {
compute_expenses(df) %>%
filter(yearmon >= month_cutoff) %>%
spread(yearmon, expenses, fill=0) %>%
print_tibble_rows()
}
compute_total <- function(df) {
full_join(compute_income(prune_coa(df)) %>% select(-account),
compute_expenses(prune_coa(df)) %>% select(-account),
by=c("yearmon", "commodity")) %>%
mutate(income = ifelse(is.na(income), 0, income),
expenses = ifelse(is.na(expenses), 0, expenses),
net = income - expenses) %>%
gather(type, amount, -yearmon, -commodity)
}
print_total <- function(df) {
compute_total(df) %>%
filter(yearmon >= month_cutoff) %>%
spread(yearmon, amount, fill=0) %>%
print_tibble_rows()
}
print_total(df)
## # A tibble: 3 × 5
## commodity type `Sep 2021` `Oct 2021` `Nov 2021`
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 USD expenses 7408. 7453. 2227.
## 2 USD income 9437. 9279. 4640.
## 3 USD net 2028. 1826. 2413.
print_income(prune_coa(df, 2))
## # A tibble: 1 × 5
## account commodity `Sep 2021` `Oct 2021` `Nov 2021`
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 Income:US USD 9437. 9279. 4640.
print_expenses(prune_coa(df, 2))
## # A tibble: 6 × 5
## account commodity `Sep 2021` `Oct 2021` `Nov 2021`
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 Expenses:Financial USD 4 39.8 4
## 2 Expenses:Food USD 504. 502. 134.
## 3 Expenses:Health USD 194. 194. 96.9
## 4 Expenses:Home USD 2602. 2614. 0
## 5 Expenses:Taxes USD 3984. 3984. 1992.
## 6 Expenses:Transport USD 120 120 0
print_income(df)
## # A tibble: 3 × 5
## account commodity `Sep 2021` `Oct 2021` `Nov 2021`
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 Income:US:ETrade:GLD:Dividend USD 157. 0 0
## 2 Income:US:Hoogle:GroupTermLife USD 48.6 48.6 24.3
## 3 Income:US:Hoogle:Salary USD 9231. 9231. 4615.
print_expenses(df)
## # A tibble: 19 × 5
## account commodity `Sep 2021` `Oct 2021` `Nov 2021`
## <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 Expenses:Financial:Commissions USD 0 35.8 0
## 2 Expenses:Financial:Fees USD 4 4 4
## 3 Expenses:Food:Groceries USD 249. 230. 68.5
## 4 Expenses:Food:Restaurant USD 256. 272. 65.2
## 5 Expenses:Health:Dental:Insurance USD 5.8 5.8 2.9
## 6 Expenses:Health:Life:GroupTermLife USD 48.6 48.6 24.3
## 7 Expenses:Health:Medical:Insurance USD 54.8 54.8 27.4
## 8 Expenses:Health:Vision:Insurance USD 84.6 84.6 42.3
## 9 Expenses:Home:Electricity USD 65 65 0
## 10 Expenses:Home:Internet USD 80.0 79.9 0
## 11 Expenses:Home:Phone USD 56.8 68.6 0
## 12 Expenses:Home:Rent USD 2400 2400 0
## 13 Expenses:Taxes:Y2021:US:CityNYC USD 350. 350. 175.
## 14 Expenses:Taxes:Y2021:US:Federal USD 2126. 2126. 1063.
## 15 Expenses:Taxes:Y2021:US:Medicare USD 213. 213. 107.
## 16 Expenses:Taxes:Y2021:US:SDI USD 2.24 2.24 1.12
## 17 Expenses:Taxes:Y2021:US:SocSec USD 563. 563. 282.
## 18 Expenses:Taxes:Y2021:US:State USD 730. 730. 365.
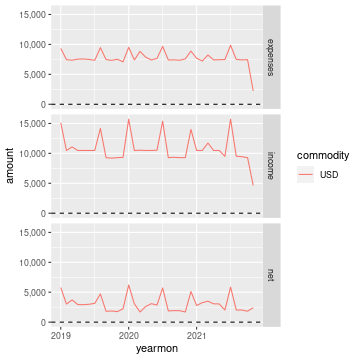
## 19 Expenses:Transport:Tram USD 120 120 0And here is a plot of income, expenses, and net income over time:
ggplot(compute_total(df), aes(x=yearmon, y=amount, group=commodity, colour=commodity)) +
facet_grid(type ~ .) +
geom_line() + geom_hline(yintercept=0, linetype="dashed") +
scale_x_continuous() + scale_y_continuous(labels=scales::comma)